Water treatment has come a long way from its early days of simple filtration and chlorination. Today, advanced technologies and sustainable chemical solutions are employed to address a wide range of contaminants and ensure water safety. Brainerd Chemical is proud to lead the way in developing biodegradable and non-toxic chemicals and processes to help our customers achieve more responsible water treatment operations.
The Rise of Peracetic Acid
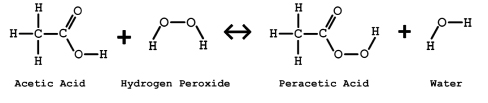
Peracetic acid (PAA) is an organic peroxide with strong oxidizing properties. It is produced by reacting acetic acid with hydrogen peroxide. PAA has gained popularity in water treatment due to its effectiveness, versatility, and environmental benefits.
PAA is a broad-spectrum disinfectant that is highly effective against a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Its strong oxidizing potential allows it to break down cell walls and disrupt cellular functions, leading to rapid disinfection¹.
Unlike chlorine-based disinfectants, PAA does not produce harmful disinfection by-products. This is a significant advantage, as DBPs like trihalomethanes (THMs) and haloacetic acids (HAAs) have been associated with health risks².
PAA decomposes quickly into acetic acid, water, and oxygen, leaving no harmful residues. This makes it an environmentally friendly option for water treatment². And, PAA maintains its efficacy across a wide pH range and is less affected by the presence of organic matter compared to other disinfectants. This makes it suitable for diverse water treatment applications¹.
Applications of Peracetic Acid
Peracetic acid’s versatility makes it a valuable tool increasingly used for water treatment due to its effectiveness and environmental benefits. A wide range of industries use PAA to improve operational efficiency and achieve greater environmentally responsible operations such as:
Municipal Wastewater Treatment
PAA is increasingly used in municipal wastewater treatment plants to disinfect effluent before discharge into water bodies. Its rapid action and minimal environmental impact make it an attractive alternative to chlorine².
Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage industry, PAA is used to sanitize equipment, surfaces, and packaging materials. Its ability to break down into harmless by-products ensures that there is no risk of contamination³.
Oil & Gas
PAA is use as a biocide to control bacteria in water systems, reduce microbial contamination, control hydrogen sulfide levels, reduce iron sulfide emulsions and scale, as well as treat produced and flow-back water allowing for more sustainable operations that are less dependent upon fresh water.
Healthcare
PAA is employed in healthcare settings for sterilizing medical instruments and surfaces. Its broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and rapid action are crucial for maintaining hygiene and preventing infections³.
Pulp and Paper Industry
PAA is used for bleaching and disinfecting paper products. Its strong oxidizing properties help achieve high levels of whiteness and microbial control⁴.
Cooling Towers
PAA is used in cooling towers to control microbial growth and biofilm formation. Its effectiveness in varying water conditions and rapid decomposition make it a preferred choice for maintaining system efficiency⁴.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Peracetic acid (PAA) is a safe and powerful oxidizing agent offering significant benefits. The Brainerd Chemical team helps our customers expand the use of this eco-friendly solution by overcoming commonly perceived challenges:
Handling and Safety Concerns
– Challenge: PAA is a potent chemical that requires careful handling to prevent skin burns, respiratory issues, or other safety hazards.
– Solution: Proper safety protocols, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), adequate ventilation, and proper storage practices, are critical. Additionally, training workers on safe handling procedures and emergency response can minimize risks.
Stability and Storage
– Challenge: PAA can decompose over time, especially when exposed to light or heat, which reduces its effectiveness.
– Solution: PAA should be stored in cool, dark conditions and used within its shelf life. Manufacturers often provide stabilized formulations of PAA to extend its stability.
Odor and Byproducts
– Challenge: PAA has a strong vinegar-like odor, which can be unpleasant and may cause discomfort. It can also produce acetic acid and other byproducts that may affect water quality or require further treatment.
– Solution: Proper dosing and ventilation can minimize odor issues. Additionally, the use of activated carbon or other treatment methods can help remove unwanted byproducts from treated water.
Dosing and Control
– Challenge: Precise dosing of PAA is essential for effective treatment without overuse, which can lead to excess residuals or unwanted side reactions.
– Solution: Automated dosing systems with real-time monitoring can ensure accurate application of PAA. These systems can adjust the dosage based on the water’s characteristics, such as organic load or microbial count, to optimize effectiveness.
Regulatory and Environmental Concerns
– Challenge: There may be regulatory restrictions on the use of PAA, especially regarding discharge limits for byproducts like acetic acid. Environmental impacts need careful consideration.
– Solution: Compliance with local and federal regulations is crucial. This may involve pre-treatment or post-treatment steps to ensure that discharge levels meet environmental standards. Conducting environmental impact assessments and working closely with regulators can help address these concerns.
Compatibility with Other Treatment Chemicals
– Challenge: PAA may react with other treatment chemicals, leading to reduced efficacy or the formation of harmful byproducts.
– Solution: Careful planning and coordination of chemical dosing schedules are required to avoid adverse interactions. Compatibility testing and consultation with chemical suppliers can guide the safe and effective integration of PAA into a water treatment program.
Cost
– Challenge: PAA can appear to be more expensive than other disinfectants.
– Solution: Cost concerns dissipate when considering the impact of PAA adoption across the complete water treatment operation including effectiveness, reduced safety issues, and substantially improved environmental outcomes. Additionally, optimizing the dosing and using PAA in conjunction with other treatment methods often reduces overall costs.
Learn How to Integrate PAA Into Your Operations
Organizations can take advantage of the benefits of PAA while minimizing potential downsides. There are a variety of resources available to learn more about implementing peracetic acid solutions for water treatment. The upcoming Association of Water Technologies (AWT) Annual Convention & Exposition in Louisville, KY is an ideal resource. A host of experts will be on hand including water treatment specialists from Brainerd Chemical Company. Attend educational sessions to build the skills that can have an immediate effect on the future direction of your business—and impact your bottom line. And the Exposition Hall offers a glimpse of the latest industry advances and live demonstrations of products and technologies that are changing the field of water treatment.
Looking Forward
The future of water treatment is promising with peracetic acid emerging as an effective and sustainable tool, offering broad-spectrum disinfection and minimal environmental impact. Its versatility makes it suitable for various applications across multiple industries, including municipal wastewater treatment, food and beverage, healthcare, pulp and paper, oil and gas, and cooling towers.
Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving its stability, reducing costs, and expanding applications. to help industries prioritize environmentally responsible operations through sustainable water treatment solutions.
By embracing innovative technologies like peracetic acid, the water treatment industry can continue to evolve and meet the growing demands for safe and clean water through environmentally responsible solutions.
About Brainerd Chemical Company:
Brainerd Chemical Company is one of the largest independent suppliers of chemicals and related services in the continental United States, manufacturing, blending, packaging and distributing chemical products to a wide variety of industrial sectors.
Media Inquiries:
Brainerd Chemical Company: 1+ (918) 622-1214
SOURCE: Brainerd Chemical Company
1 Emerging Trends In Disinfection Peracetic Acid – Water Online. https://www.wateronline.com/doc/emerging-trends-in-disinfection-peracetic-acid-0001.
2 How peracetic acid is changing wastewater treatment. https://cen.acs.org/environment/water/peracetic-acid-changing-wastewater-treatment/98/i15.
3 What You Need To Know About Peracetic Acid (PAA) For Water Treatment …. https://www.blue-white.com/article/what-you-need-to-know-about-peracetic-acid-paa-for-water-treatment/.
4 Formation of Halogenated Byproducts upon Water Treatment with Peracetic …. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/acs.est.1c06118.